Phages exhibit two different types of life cycle. Both lytic and lysogenic bacteriophage begin a replication cycle when contact is made with a suitable host bacterium.
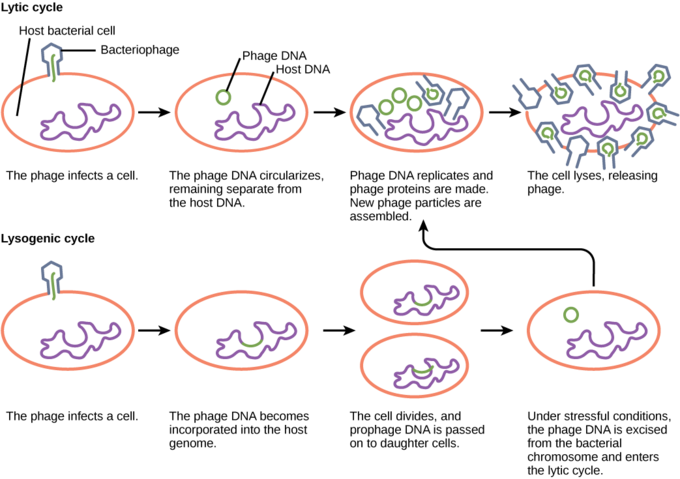
21 2b The Lytic And Lysogenic Cycles Of Bacteriophages Biology Libretexts
Get integrated into the host DNA during the lysogenic cycle.

. Lysogenic phage form a prophage by integrating into a bacterial chromosome. This takes place within the host cell and the virus takes control of the host cell and controls its cellular mechanism to reproduce itself. In the lysogenic cycle the DNA is only replicated not translated into proteins.
Phage injects its DNA into cell wall 3 replication. Temperate Bacteriophages and the Lysogenic Cycle. When a lysogenic bacterium exposed to UV-light or a chemical the prophage withdraw from the host DNA to undergo lytic cycle.
In this cycle intra-cellular multiplication of the phage results in the lysis of host bacteria resulting in release of progeny virions. The host bacterium containing prophage is called a lysogenic bacterium or lysogen. Within a lysogenic cycle the nucleic acid of the bacteriophage is.
Upon induction by an appropriate stimulus the phage DNA is removed and enters a lytic cycle. Viral DNA takes control on hosts biosynthetic machinery 4 lysis. The lysogenic cycle or the lytic cycle.
When a temperate bacteriophage infects a bacterium it can either replicate by means of the lytic life cycle and cause lysis of the host bacterium or it can incor View the full answer. Filamentous phage such as male specific phage 13 are released by budding and do not kill host cell. Bacteriophages capable of a lysogenic life cycle are termed temperate bacteriophages.
In this cyclephage DNA becomes integrated with the bacterial genome and replicates with the. Please use one of the following formats to cite this article in your essay paper or report. Lytic or lysogenic replication.
It is the reproduction of viral cells. Lysogenic cycle It involves the incorporation of the viral genome into the genome of the host cell infecting it from within. The main difference between the lytic and lysogenic cycles of bacteriophage reproduction is that during the lytic cycle the bacteriophage enters the host cell as a separate component that does not integrate with the host DNA whereas in the lysogenic cycle the bacteriophage DNA is integrated into the host DNA and replicates accordingly.
Bacteriophage may replicate by lytic and lysogenic cycles. Occur as an independent unit during the lytic cycle. The lytic cycle consists of 1 attachment.
The prophage passively replicates along with the host DNA for many generations. Phages can undergo two types of replication. Lysogeny is characterized by integration of the bacteriophage nucleic acid into the host bacteriums genome or formation of a circular replicon in the bacterial cytoplasm.
Lysogenic cycle can happen after the lytic cycle whereas the viral DNA is still present but in a dormant state. Two major cycles of multiplication of bacteriophages are. Once a bacteriophage attaches to a susceptible host it pursues one of two replication strategies.
So again these stages are and again during. Lysogenic cycle is characterized by integration of the bacteriophages or phages as they are commonly known are viruses that specifically infect bacteria nucleic acid into the host bacteriums genome or formation of a circular replicon in the bacterial cytoplasm. Tail release enzyme lysozyme to dissolve bacterial cell wall.
Phage injects its DNA into cell wall 3 replication. The lytic and lysogenic cycles are well studied in bacteriophages as they are an ideal model to study the viruss life cycle. During integration into host genes the phage loses genes required for replication this prevents the induction of the lytic cycle and killing of host bacteria.
It is a method by which a virus can replicate its DNA by utilizing the cell of the host. Lysogenic conversion is mediated by the transduction of bacterial genes from the donor bacterium to the recipient bacterium by bacteriophages. The lysogenic cycle is a method by which a virus can replicate its DNA using a host cell.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Attach to receptor site on bacterial cell wall by weak linkage 2 penetration. 100 1 rating Answer- Difference between lytic and lysogenic replication of bacteriophages- Lytic replication of bacteriophages Lysogenic replication of bacteriophages In lytic cycle bacteriophage destruct membrane and cellular structure of infected bacteria and v.
In the lysogenic pathway the phage DNA is integrated as a prophage into the host genome and replicated along with it. Temperate phages in addition to following a. Lysogenic cycle also called lysogeny is one of two cycles of viral reproduction the lytic cycle being the other.
The action of most of viral genes is to enable the viruses to infect their respective host cells multiply by using the host machinery such as enzymes and ribosomes and then causing the lysis of cells. Phages such as T4 which cause the lysis of their cells are termed virulent phages. Lytic cycle is active viral replication causing the host to feel viral symptoms.
Lysogeny or the lysogenic cycle is one of two cycles of viral reproduction. The lytic cycle and the lysogenic cycle are means of viral replication. In this cycle the reproduction of virus comprises the fusion of the nucleic acid of a bacteriophage with that of a host which is succeeded by proliferation of the prophage produced.
In the lysogenic cycle it is only the DNA which gets replicated and does not get translated into proteins. Also known as temperate cycle. In this condition the bacterium continues to live and reproduce normally while the bacteriophage lies in a dormant state in the.
Also known as virulent cycle. During a lytic replication cycle a phage attaches to a susceptible host bacterium introduces its genome into the host cell cytoplasm and utilizes the ribosomes of the host to manufacture its proteins. Lysogenic cycle is one of the two reproductive cycles of bacteriophage that integrates the bacteriophage nucleic acid into the genome of the host bacterium.
Typically viruses can undergo two types of DNA replication.

Lytic Vs Lysogenic Understanding Bacteriophage Life Cycles Technology Networks

Lytic Vs Lysogenic Understanding Bacteriophage Life Cycles Technology Networks

Life Cycle Of An Obligately Lytic Bacteriophage As This Is A Cycle Download Scientific Diagram
0 Comments